...
6.3 LWM2M (AMIT S / PADHU)
6.3.1 Overview and objective of project...
6.3.2 API's defined
6.4 OneM2M (ELIZABETH to identify lead)
6.4.1 Overview and objective of project...
...
LWM2M
Overview
The OMA LWM2M (Light Weight Machine To Machine) protocol provides the capability for applications to communicate and manage IoT devices. LWM2M is based on the IETF Constrained Application Protocol (CoAP) providing communication between a LWM2M Server and a LWM2M Client (where Client is located in a constrained IoT device).
Key features
Some of the abilities which are helpful from connected car perspective from LWM2M are the following:
- Low data byte transmission with allowance for client to sleep (i.e., non-continuous communication)
- Suitable for constrained devices (hence reduced footprint for reduced CAPEX for car manufacturers)
- Several objects can be reported in one message using simple content types like TLV, JSON and single objects with simple text content type
- Ability to support a range of solutions through pre-defined objects (connected car objects/resources)
- Client (connected car) could send notifications to server based on defined trigger events e.g. periodic reporting, reporting upon change of value, reporting based on thresholds reached. This is key as it gets past the poll and/or notification model
- LWM2M by default works with 3GPP technologies hence easier integration with telecommunication operators
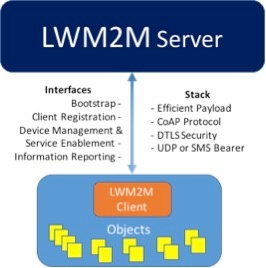
Core Interfaces
The core interfaces between the server and the client are categorized into:
- Bootstrap
- Client Registration
- Device management and service enablement
- Information Reporting
Features
OMA LWM2M is unique in that aspect, that it converges both management and application control functionality within one communication session allowing for efficient handling of IoT devices. Since OMA LWM2M protocol is based on IETF CoAP, the OMA LWM2M protocol allows different transport bindings (e.g., UDP, SMS) and is secured using IETF DTLS protocol.
The device management features defined by OMA for release 1.0 of LWM2M are:
- Access control on the specific contents that could be handled remotely by different entities
- Software / firmware Management for applications inside the Client
- Lock & Wipe of the device from misuse
- Connection management for choosing various radio methods by the Client
- Device Capability Management to identify the capabilities existing in the device
- Location of the device
- Connection Statistics in terms of communication characteristics over the air
The object registry provides a unique way of identifying the necessary and relevant objects. The object registry is maintained by OMNA (Open Mobile Naming Authority). It includes categories for interleaving 3rd party management objects and application objects into the OMNA system from vendors and other standards organizations (for e.g., IPSO Alliance and oneM2M)
6.5 GENIVI Remote Vehicle Interaction (RUDI S to collaborate with Magnus/Magnus)
...